Search This Blog
Tuesday, 14 April 2015
Saturday, 11 April 2015
How to Remove Given Character From String in Java - Recursion
Write a program to remove a given character from String in Java. Your program must remove all occurrences of given character. For example, if given String is "aaaaa" and String to remove is "a" then output should be an empty String. Similarly if input String is "abc" and character to remove is "b" then your program must return "ac" as output. You are not allowed to use any JDK method or third party method which solves this method directly, but you can use basic String manipulation method like indexOf(), toChar() or substring() from java.lang.String class. Most important thing is, you must code the logic to solve the problem by yourself. You should also write the solution using both Iterative and Recursive algorithms. An Iterative algorithm is the one which make use of loops e.g. for loop, while loop or do while loop, which recursive solution should not use any loop. Now let's think how can we solve this problem? Most simple solution which comes in my mind is to iterate over String by converting into character array and check if current character is same as given character to remove or not, if it is then ignore it otherwise add character into StringBuilder. At the end of iteration you will have a StringBuilder with all character except the one which is asked to remove, just convert this StringBuilder to String and your solution is ready. This solution should have space complexity of O(n) because you need an extra buffer of same size as original String and time complexity will also be O(n) because you need to loop over all elements of String. Can you make it better? because this solution will not work for large String, especially if you have memory constraint. Now, let's see how to remove character from String recursively?BTW, this is one of the good coding question and has been asked in companies like Goldman Sachs, Amazon and Microsoft. So if you are preparing for programming job interviews, make sure you include this question in your list as well.
Removing a given Character From String Recursively
In order to solve this problem recursively, we need a base case and a process which reduce the problem space after each recursive step. We can solve this problem using indexOf() and substring() method of Java's String class, indexOf() method returns index of a given character if its present in the String on which this method is called, otherwise -1. So first step, we will try to find the index of given character, if its present then we will remove it using substring() method, if not present then it become our base case and problem is solved.
Here is our sample program to recursively remove all occurrences of a given character.
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;/*** Java program to remove given character from a given String using loops and recursion,* asked as coding question to Java programmers.**/public class RemoveCharFromString {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RemoveCharFromString.class);public static String remove(String word, char unwanted){StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();char[] letters = word.toCharArray();for(char c : letters){if(c != unwanted ){sb.append(c);}}return sb.toString();}public static String removeRecursive(String word, char ch){int index = word.indexOf(ch);if(index == -1){return word;}return removeRecursive(word.substring(0, index) + word.substring(index +1, word.length()), ch);}}
You can see that we have two method, both accept one String and a character which needs to be removed from the given String. The first method, remove(String word, char unwanted) deletes the given character using iteration while second method removeRecursive(String word, char ch), uses recursion to accomplish this task.
Unit Testing of Solution
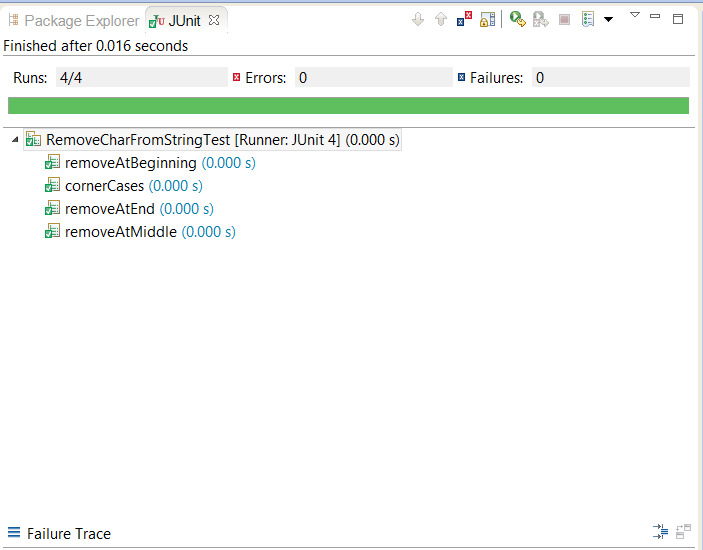
Here is our suite of JUnit tests to check whether this program is working properly or not. We have unit test to check removing a character from beginning, middle and end. We also have unit test for corner cases like removing the only character String contains, or removing character from String which contains same character multiple times. You can also add other tests for checking with empty String, NULL and trying to remove a character which is not present in the String. One thing to note here is that, we are testing both of our remove() method, one which removes given character using iteration and other which removes specified character using recursion.
import static org.junit.Assert.*;import org.junit.Test;/*** JUnit test to for unit testing our remove() utility method, which accepts* an String and a character, to remove all occurrences of that character*/* from that String.public class RemoveCharFromStringTest {@Testpublic void removeAtBeginning(){assertEquals("bc", RemoveCharFromString.remove("abc", 'a'));assertEquals("bc", RemoveCharFromString.removeRecursive("abc", 'a'));assertEquals("bcdefgh", RemoveCharFromString.removeRecursive("abcdefgh", 'a'));assertEquals("bcdefgh", RemoveCharFromString.removeRecursive("abcdefgh", 'a'));}@Testpublic void removeAtMiddle(){assertEquals("abd", RemoveCharFromString.remove("abcd", 'c'));assertEquals("abd", RemoveCharFromString.removeRecursive("abcd", 'c'));}@Testpublic void removeAtEnd(){assertEquals("abc", RemoveCharFromString.remove("abcd", 'd'));assertEquals("abc", RemoveCharFromString.removeRecursive("abcd", 'd'));}@Testpublic void cornerCases(){// empty string testassertEquals("", RemoveCharFromString.remove("", 'd'));// all removable character testassertEquals("", RemoveCharFromString.remove("aaaaaaaaaaaaaa", 'a'));// all but one removable charactersassertEquals("b", RemoveCharFromString.remove("aaaaaaaaaaaaaab", 'a'));}}
Testsuite: RemoveCharFromStringTest
Tests run: 4, Failures: 0, Errors: 0, Time elapsed: 0.172 sec
That's all about how to remove a given character from given String in Java. This is a question which often appears in various Java interviews, written test and telephonic round. You should remember both iterative and recursive algorithm to solve this problem and pros and cons of each approach.
Sunday, 5 April 2015
How to delete a directory with files in Java - Example
Deleting an empty directory is easy in Java, just use delete() method of java.io.File
class, but deleting a directory with files is unfortunately not easy.
You just can't delete a folder if it contains files or sub folders. Calling delete() method on a File instance representing a non empty directory will just return false without removing the directory. In order to delete this
folder, you need to delete all files and sub directories inside this
folder. This may seem cumbersome, but unfortunately there is no method
which can delete directory with files in Java, not even on Java 7 Files and Paths class. So there is two choices, either you write your own method to recursively delete all files and folder before deleting a directory or alternatively you
can use an open source utility library like Apache Commons IO which
will do this for you. BTW, If you have to do this without using any
third party library than you can use the example shown in this tutorial.
You know what, I have asked this question couple of times to Java developers and only 3 out of 10 knows that you cannot delete directory with files in Java.
I am not surprised because this is the kind of detail which is not
obvious. Until you do it, you don't know this. Java isn't able to delete
folders with data in it. You have to delete all files before deleting the folder. There also unfortunately no direct method to delete a directory with files. Though, In JDK 7 you could use Files.walkFileTree() and Files.deleteIfExists() to delete a tree of files.
Java Program to delete non empty directory in Java
Primary method to delete a file or directory in Java was File.delete() method form java.io
package. This method can be used to delete a file or a nonempty
directory but fail silently when it comes to deleting folder with files.
If you ignore return value of this method, which is false if it failed
to delete directory then you will never know that whether your program
failed to remove some directory and I have seen many developers hit by
this bullet. Thankfully, JDK 7 added another delete() method in Files utility class to delete file and directory, which throws IOException
when a file cannot be deleted. This is really useful for
troubleshooting purpose e.g. to find out why a file cannot be deleted.
There is one more similar method, Files.deleteIfExists(), which is slightly more readable than original delete() method from File class.
Now coming back to our original question, how to delete a folder with files or sub folder inside it. Well, we need to write a program which can recursively check all files and folder and delete them before deleting the top level directory. In this example, I have create a directory structure with one directory containing a file and a sub-directory containing another file and tried to delete the top directory using our method.
 In this program, I have two overloaded method, deleteDirectory(File file) and deleteDirectory(String path)
to demonstrate the right and wrong way to delete a directory in Java.
The method which accepts a String argument, first print all contents of
directory without printing contents of sub directory and then just call
delete method on the directory we want to delete. This method cannot
remove a non-empty directory, so it failed and return false
which is captured in method. The right way to delete a directory with
files is to recursively delete any sub directory and files inside it,
which is demonstrated in deleteDirectory(File)
method. This method first check if the given File instance represent a
directory, if yes then it list all files and sub directory and recursively call the same method to delete each of them. This allows program to remove files inside a sub folder before removing it. Once everything inside given directory is deleted, it proceed to delete the given folder.
In this program, I have two overloaded method, deleteDirectory(File file) and deleteDirectory(String path)
to demonstrate the right and wrong way to delete a directory in Java.
The method which accepts a String argument, first print all contents of
directory without printing contents of sub directory and then just call
delete method on the directory we want to delete. This method cannot
remove a non-empty directory, so it failed and return false
which is captured in method. The right way to delete a directory with
files is to recursively delete any sub directory and files inside it,
which is demonstrated in deleteDirectory(File)
method. This method first check if the given File instance represent a
directory, if yes then it list all files and sub directory and recursively call the same method to delete each of them. This allows program to remove files inside a sub folder before removing it. Once everything inside given directory is deleted, it proceed to delete the given folder.
That's all on how to delete non empty directory with files in Java. As you can see in output that method which takes String path is not able to delete our directory with files "one", instead it failed, while our second method has recursively deleted everything inside this top level directory, you can see files are deleted before directory to make them empty. I have not tested this code heavily but it should work on all Java version starting from Java 1.2. It is not using any JDK 7 method e.g. Files.delete() or Files.deleteIfExists() so you can use it with Java 1.5 and Java 1.6 as well. Just remember that you cannot delete a folder with files in Java without removing everything inside it.
Now coming back to our original question, how to delete a folder with files or sub folder inside it. Well, we need to write a program which can recursively check all files and folder and delete them before deleting the top level directory. In this example, I have create a directory structure with one directory containing a file and a sub-directory containing another file and tried to delete the top directory using our method.
 In this program, I have two overloaded method, deleteDirectory(File file) and deleteDirectory(String path)
to demonstrate the right and wrong way to delete a directory in Java.
The method which accepts a String argument, first print all contents of
directory without printing contents of sub directory and then just call
delete method on the directory we want to delete. This method cannot
remove a non-empty directory, so it failed and return false
which is captured in method. The right way to delete a directory with
files is to recursively delete any sub directory and files inside it,
which is demonstrated in deleteDirectory(File)
method. This method first check if the given File instance represent a
directory, if yes then it list all files and sub directory and recursively call the same method to delete each of them. This allows program to remove files inside a sub folder before removing it. Once everything inside given directory is deleted, it proceed to delete the given folder.
In this program, I have two overloaded method, deleteDirectory(File file) and deleteDirectory(String path)
to demonstrate the right and wrong way to delete a directory in Java.
The method which accepts a String argument, first print all contents of
directory without printing contents of sub directory and then just call
delete method on the directory we want to delete. This method cannot
remove a non-empty directory, so it failed and return false
which is captured in method. The right way to delete a directory with
files is to recursively delete any sub directory and files inside it,
which is demonstrated in deleteDirectory(File)
method. This method first check if the given File instance represent a
directory, if yes then it list all files and sub directory and recursively call the same method to delete each of them. This allows program to remove files inside a sub folder before removing it. Once everything inside given directory is deleted, it proceed to delete the given folder. import java.io.File;
/**
* Java Program to delete directory with sub directories and files on it
* In this example, we have a directory tree as one/ abc.txt
* two/ cde.txt and we will try to delete top level directory one here.
*/
public class FileDeleteDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
deleteDirectory("one"); // wrong way to remove a directory in Java
deleteDirectory(new File("one")); //right way to remove directory in Java
}
/*
* Right way to delete a non empty directory in Java
*/
public static boolean deleteDirectory(File dir) {
if (dir.isDirectory()) {
File[] children = dir.listFiles();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
boolean success = deleteDirectory(children[i]);
if (!success) {
return false;
}
}
}
// either file or an empty directory
System.out.println("removing file or directory : " + dir.getName());
return dir.delete();
}
/*
* Incorrect way to delete a directory in Java
*/
public static void deleteDirectory(String file) {
File directory = new File(file);
File[] children = directory.listFiles();
for (File child : children) {
System.out.println(child.getAbsolutePath());
}
// let's delete this directory
// it will not work because directory has sub-directory
// which has files inside it.
// In order to delete a directory,
// you need to first delete its files or contents.
boolean result = directory.delete();
if (result) {
System.out.printf("Directory '%s' is successfully deleted",
directory.getAbsolutePath());
} else {
System.out.printf("Failed to delete directory '%s' %n",
directory.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
D:\Programs\Test\one\abc.txt
D:\Programs\Test\one\two
Failed to delete directory 'D:\Programs\Test\one'
removing file or directory : abc.txt
removing file or directory : cde.txt
removing file or directory : two
removing file or directory : one
That's all on how to delete non empty directory with files in Java. As you can see in output that method which takes String path is not able to delete our directory with files "one", instead it failed, while our second method has recursively deleted everything inside this top level directory, you can see files are deleted before directory to make them empty. I have not tested this code heavily but it should work on all Java version starting from Java 1.2. It is not using any JDK 7 method e.g. Files.delete() or Files.deleteIfExists() so you can use it with Java 1.5 and Java 1.6 as well. Just remember that you cannot delete a folder with files in Java without removing everything inside it.
Introduction of How Android Works for Java Programmers
Android development is current buzz in Java programming world. It's the
Android, which keeps Java in the fore front from last couple of years. Now, How
important is to understand or learn Android for Java programmers? Well it
depends, if you like application development and want to reach mass, Android
offers that opportunity to you. Millions of Android phones are available and
they are keep increasing, with pace, much higher than IPhone or iOS. What all
these means is, it does make a lot of sense to learn Android programming for
Java programmer, and this article is about that, but this is also a one of
the good reason to learn Java programming.
This tutorial will give you basic idea of How
Android works? not detailed but a good overview. One distinct advantage
Java programmers has over others is that Android API is much like Java API,
though Android doesn't support all classes available in J2SE SDK, it supports
critical ones. Another advantage is that, you can use same tools e.g. IDE like
Eclipse to develop Android applications, Google provides Eclipse plug-in for
Android development. On opposite, if you want to go for iOS development, A steep learning curve with
Objective C and iOS SDK waits you. I think it make more sense for a C++
programmer to do Objective C and iOS, than a Java Programmer. So classic battle
of Java vs C++ still continues with Smartphone application development. Any
way, let's come to the topic of How Android works internally. . If you are
looking for some good books to start with Android, you can also check out Professional Android 4 Application Development and Ian F. Darwin’s Android Cookbook.
How Android works
 As I said Android uses Java for application development. So you can code
your Android apps using Java API provided by Google, and it compiles into class
files. Similarity ends here, Android doesn't use Java Virtual machine (JVM) for
executing class files, instead it uses Dalvik
virtual machine, which is not a true JVM and doesn't operate on Java byte
code. In order to run on Dalvik Virtual machines, class files are further
compiled into Dalvik Executable or DEX
format. After conversion to DEX format, class files along with other
resources are bundled into Android Package (APK) for
distribution and installation into various devices. Key thing to know is that,
Dalvik VM is based on subset of the Apache Harmony Project for its core class
library, which means it doesn't support all J2SE API. If you are using Eclipse
IDE for coding Android Apps, then you don't need to worry much because, it will
help you with code completion. Now let's see How Android Application runs on device?
As I said Android uses Java for application development. So you can code
your Android apps using Java API provided by Google, and it compiles into class
files. Similarity ends here, Android doesn't use Java Virtual machine (JVM) for
executing class files, instead it uses Dalvik
virtual machine, which is not a true JVM and doesn't operate on Java byte
code. In order to run on Dalvik Virtual machines, class files are further
compiled into Dalvik Executable or DEX
format. After conversion to DEX format, class files along with other
resources are bundled into Android Package (APK) for
distribution and installation into various devices. Key thing to know is that,
Dalvik VM is based on subset of the Apache Harmony Project for its core class
library, which means it doesn't support all J2SE API. If you are using Eclipse
IDE for coding Android Apps, then you don't need to worry much because, it will
help you with code completion. Now let's see How Android Application runs on device?How Android apps runs on Device
If you are familiar with Linux and concept of process, then it's easy to
understand how android applications runs. By default, Each Android application
is assigned a unique user id by the Android operating system. After starting
android application, they run on there own process, inside there own virtual
machine. Android operating system manages starting and shutting down the
application process, whenever required. This means, each android application
runs in isolation with other, but they can certainly request access to hardware
and other system resources. If you are familiar with mobile application
development, may be in J2ME, then you may know about permissions. So when an
android application is installed or started, it request necessary permission
required to connect internet, phone book and other system resource. User
explicitly provides grant these permissions, or it may deny. All these
permissions are defined in manifest file of Android application. Unlike Java
Manifest file, Android manifest is an XML file, which lists all the
components of apps, and settings for those components. Four major components of
Android application development is Activities, Services, Content Providers and Broadcast Receivers. Activity is most common of them, as it represent a single
screen in Android Application. For example, in an Android Game, you can have
multiple screens for login, high score, instructions and game screen. Each of
these screen represent different Activities inside
your app. Similar to Java, good thing about Android is that it manages certain
task on behalf of developer, one of them is creating activity object.
Activities are managed by System, when you want to start an activity, you call startActivity() method
which takes an Intent object. In response to this call, System can either
create new activity object or reuse an existing one. Just like Garbage collection in Java,
manages a critical task or reclaiming memory, Android manages starting,
stopping, creating and destroying of apps by themselves. You may think it's
restrictive, but it's not. Android provides life-cycle events, which you can
override to interact with this process.
That's all on How Android works.
Android is definitely worth learning for Java programmer, as it uses
Java, you can reuse your existing knowledge of Java programming techniques, design patterns and best practices to code a good
android app. Of course, you need to adapt some Android specific things like,
but those will come along. So, what are you waiting for, go and explore more
about Android and write an Android HelloWorld application. Finally you can also
take a look some of the best book to start with Android development, Professional Android 4 Application Development and Android Cookbook by Ian F.
Darwin.
Tuesday, 31 March 2015
10 difference between Java and JavaScript for Programmers
Programmers, developers and internet users have always been confused between Java and JavaScript. Many people still thinks that JavaScript is part of Java platform, which is not true. In truth, JavaScript has nothing to do with Java, only common thing between them is word "Java", much like in Car and Carpet, or Grape and Grapefruit. JavaScript is a client side scripting languagefor HTML, developed by Netscape, Inc, while Java is a programming language, developed by Sun Microsystems. James Gosling is Inventor of Java, popularly known as father of Java. While in today's world calling JavaScript just a client side scripting language would not be good, as its now been used in servers also using node.js and people are doing object oriented development in JavaScript, but that was what it was originally developed. There are several difference between Java and JavaScript, from how they are written, compiled and executed. Even capability of Java and JavaScript vary significantly. Java is full feature Object oriented programming language, used in almost everywhere, starting from programming credit card to server side coding. Android uses Java as programming language for creating Android apps, Swing is a Java API used to create desktop applications and Java EE is a Java platform for developing web and enterprise applications. On the other hand JavaScript is primarily used to bring interactivity into web pages, though there are other alternatives like Flash, JavaScript is the most popular one and regaining lots of ground lost earlier with introduction of powerful and easy to use libraries like jQuery and jQuery UI. You can use JavaScript to validate user input, create animation and cool effects in HTML page and can do lot of interactive stuff e.g. reacting on button click, mouse movement, image click etc. In this article, I will share some key differences between Java and JavaScript, mostly from a programmers perspective.
Here is my list of key differences between JavaScript and Java as programming languages. I have worked both on them, mainly used Java for all Server Side development, Android and JavaScript for writing client side scripts to do validation, interactivity, animation and ajax calls.
1) Execution Environment
First difference between Java and JavaScript is that Java is compiled + interpreted language, Java code is fist compiled into class files containing byte code and than executed by JVM, on the other hand JavaScript code is directly executed by browser. One more difference which comes form this fact is that, Java is run inside JVM and needs JDK or JRE for running, on there other hand JavaScript runs inside browser and almost every modern browser supports JavaScript.
2) Static vs Dynamic Typed language
Another key difference between JavaScript and Java is that, JavaScript is a dynamic typed language, while Java is a statically typed language. Which means, variables are declared with type at compile time, and can only accept values permitted for that type, other hand variables are declared using vary keyword in JavaScript, and can accept different kinds of value e.g. String, numeric andboolean etc. When one variable or value is compared to other using == operator, JavaScript performs type coercion. Though it also provides === operator to perform strict equality check, which checks for type as well. See here for more differences between == and == operator in JavaScript.
3) Support of Closures
JavaScript supports closures, in form of anonymous function. In simple words, you can pass a function as an argument to another function. Java doesn't treat method as first class citizen and only way to simulate closure is by using anonymous class. By the way Java 8 has brought real closure support in Java in form of lambda expression and this has made things much easier. It's very easy to write expressive code without much clutter in Java 8.
4) OOP
Java is an Object Oriented Programming language, and though JavaScript also supports class and object, it's more like an object oriented scripting language. It's much easier to structure code of large enterprise application in Java then JavaScript. Java provides packages to group related class together, provides much better deployment control using JAR, WAR and EAR as well.
5) Right Once Run Anywhere
Java uses byte code to achieve platform independence, JavaScript directly runs on browser, but code written in JavaScript is subject to browser compatibility issue i.e. certain code which work in Mozilla Firefox, may not work in Internet Explorer 7 or 8. This is because of browse based implementation of JavaScript. This was really bad until jQuery comes. Its a JavaScript library which helps to free web developers from this browser compatibility issues. This is why I prefer to write code using jQuery rather than using plain old JavaScript code, even if its as simple as calling getElementById() or getElementByName() methods to retrieve DOM elements.
7) Block vs Function based Scoping
Java mainly uses block based scoping i.e. a variable goes out of scope as soon as control comes out of the block, unless until its not a instance or class variable. On the other hand JavaScript mainly uses function based scoping, a variable is accessible in the function they are declared. If you have a global variable and local variable with same name, local will take precedence in JavaScript.
8) Constructors
Java has concept of constructors, which has some special properties e.g. constructor chaining and ensuring that super class constructor runs before sub class, on the other hand JavaScript constructors are just another function. There is no special rules for constructors in JavaScript e.g. they cannot have return type or their name must be same as class.
9) NullPointerException
JavaScript is much more forgiving than Java, you don't have NullPointerException in JavaScript, your variable can accept different kinds of data because of JavaScript is dynamically typed language.
10) Applicability
Last but not the least, JavaScript has it's own space, sitting cozy along with HTML and CSS in Web development, while Java is everywhere. Though both has good number of open source libraries to kick start development, but jQuery has certainly brings JavaScript on fore front.
That's all on difference between Java and JavaScript language. As I said, they are totally different language, one is a general purpose programming language, while other is scripting language for HTML. Though you can do lot of fancy stuffs using JavaScript, you still don't have features like multithreading, as compared to Java. By the way JavaScript was originally named as Livescrpit, may be due to the fact that it makes your HTML pages live, and programming world would certainly be free of this confusion, had Netscape hadn't renamed LiveScript as JavaScript.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)