Reversing an array sounds pretty easy, isn't it? It does sounds like that, because all you need to do is create an array of same size, iterate through original array from end to start and populate your new array. Boom!!, you have got an array which has elements in reverse order of original array, but problem is you have used and additional array here, which makes space complexity of your solutionO(n). You cannot use this solution if array is big e.g. an array of 10 million orders and you don't have enough heap space available. Can we make it better? Can we reverse array in Java without using an additional buffer? Even If you encounter this question in your programming job interview, you will be surely asked to reverse array in place, without using an additional buffer as earlier solutiontakes lot of space. So now your task is to write a Java program to reverse an array in place. For the sake of this problem, you can assume that its an integer array (during interview, you should ask these question to your interviewer, because asking right question to fill the gap in requirement is a trait of good programmer and highly appreciated on both telephonic and face-to-face interviews). Key point to understand here is that you need to reverse the same array, you cannot use another array but one or two variable is fine. You are also not allowed to use any open source library or Java API which can reverse the array directly e.g. any method from java.util.Arrays class except Arrays.toString()to print arrays in Java. So now the requirement is clear, what approach comes in your mind? how do you solve this problem?
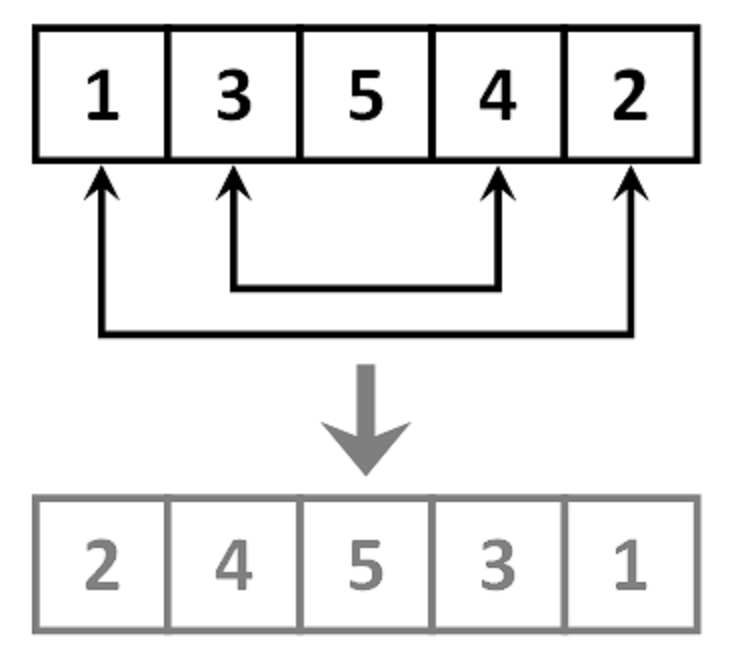
It's been said time and again that a picture is worth a thousand word and true to the point, this image explains the algorithm we used to reverse array in place quite well. You can see that how elements of arrays are swapped position with each other and middle element remain unchanged, with just two swapping we have reversed an array of five elements.
Here is our sample Java program to reverse array in place, solution is simple and easy to follow, but don't forget to look my JUnit tests to understand it bit more.
You can see in output here that input array is reversed properly and in case of null, empty and array with just one element, same array is returned.
and here is the output of running our unit tests, they all pass.
That's all about how to reverse array in place in Java. Time complexity of this method is O(n/2) or O(n) because it only iterate through half of the array, but its in O(n) because response time increases in same order as input increases. As a task, can you find a faster solution of this problem?
Java Program to Reverse Array In Place
The first thing which comes in my mind is to loop through array and swap the elements of array e.g. swap first element with last element, swap second element with second last element until you reach the middle of the array. This way, all elements of array will be reversed without using any additional buffer. Key thing to keep in mind in this algorithm is that you only need to iterate till middle element, if you go beyond that then you end up swapping elements twice and result in same array. Some of you will be puzzled, what is length of array is even? In that case there will be two middle element and we need to swap them, that's why your loop condition should be index <= middle and not index < middle. Here middle index is nothing but length/2. Remember, we are using division operator, which means if length is 8 then it will return 4 and when length is 7 it will return 3. So in case of even length, the middle element will be swapped twice, but in case of odd length there is just one middle element and it will not be swapped.It's been said time and again that a picture is worth a thousand word and true to the point, this image explains the algorithm we used to reverse array in place quite well. You can see that how elements of arrays are swapped position with each other and middle element remain unchanged, with just two swapping we have reversed an array of five elements.
Here is our sample Java program to reverse array in place, solution is simple and easy to follow, but don't forget to look my JUnit tests to understand it bit more.
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Java Program to demonstrate how to reverse an array in place.
*/
public class ArrayReversalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
reverse(numbers);
}
/**
* reverse the given array in place
* @param input
*/
public static void reverse(int[] input) {
System.out.println("original array : " + Arrays.toString(input));
// handling null, empty and one element array
if(input == null || input.length <= 1){
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < input.length / 2; i++) {
int temp = input[i]; // swap numbers
input[i] = input[input.length - 1 - i];
input[input.length - 1 - i] = temp;
}
System.out.println("reversed array : " + Arrays.toString(input));
}
}
Output
original array : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
reversed array : [7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
original array : []
original array : null
original array : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
reversed array : [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
original array : [1]
You can see in output here that input array is reversed properly and in case of null, empty and array with just one element, same array is returned.
JUnit tests
Here is my suite of JUnit tests for our reverse(int[] input) method. I have made sure to test our solution can handle null, empty array, an array with just one element, and array with even or odd number of elements. You can even test drive this problem. Writing Unit test is a good practice and during Interview you must write JUnit test even if Interview has not asked for it. This shows that you are a professional software developer and you care for your trade.import static org.junit.Assert.assertArrayEquals;
import org.junit.Test;
public class ArrayReversalDemoTest {
@Test
public void testReverseWithEvenLengthOfArray(){
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
HelloWorld.reverse(numbers);
assertArrayEquals(new int[]{6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, numbers);
}
@Test
public void testReverseWithOddLengthOfArray(){
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
HelloWorld.reverse(numbers);
assertArrayEquals(new int[]{7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, numbers);
}
@Test
public void testReverseWithEmptyArray(){
int[] numbers = {};
HelloWorld.reverse(numbers);
assertArrayEquals(new int[]{}, numbers);
}
@Test
public void testReverseWithNullArray(){
int[] numbers = null;
HelloWorld.reverse(numbers);
assertArrayEquals(null, numbers);
}
@Test
public void testReverseWithJustOneElementArray(){
int[] numbers = {1};
HelloWorld.reverse(numbers);
assertArrayEquals(new int[]{1}, numbers);
}
}
and here is the output of running our unit tests, they all pass.
That's all about how to reverse array in place in Java. Time complexity of this method is O(n/2) or O(n) because it only iterate through half of the array, but its in O(n) because response time increases in same order as input increases. As a task, can you find a faster solution of this problem?

Best explanation with example.
ReplyDeleteThanks,
https://www.flowerbrackets.com/java-program-to-swap-two-numbers/